In recent years, the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology has driven a new technological revolution, which has also brought many opportunities for innovation in the industrial field. In the machining (hereinafter referred to as machining) industry, intelligent and digital transformation is considered the key direction in solving the core pain points of the industry. Through the introduction of artificial intelligence and digital twin technology, the construction of an intelligent machining shop is becoming a reality, while intelligent CNC machine tools and their supporting solutions provide strong technical support for the transformation of the industry.
What is Digital Lisbon Technology?
Digital LiSheng technology (Digital Twin) is an advanced technology for real-time monitoring, simulation analysis, and optimization by constructing virtual models of physical entities. It replicates real-world devices, systems, or processes digitally into virtual space by integrating the Internet of Things (I0T), Big Data, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and high-performance computing technologies.

At the heart of the Digital Lisbon technology lies.
1. Physical entity: the actual equipment or system in reality.
2. Virtual model: digitized high-fidelity virtual replica.
3. Data connectivity: bi-directional data flow between physical entities and virtual models.
Through real-time data exchange, the virtual model can dynamically reflect the current state of physical entities and perform predictive analysis or optimization in the virtual space.
2. Technical components
- Sensors and data acquisition
Sensors assembled on physical entities collect data such as temperature, pressure, speed, etc. - Data processing and communication
Processing and delivering the collected data to the virtual model through cloud platform or edge computing. - Modeling and Simulation
Digital modeling tools (such as CAD) and physical simulation tools can be used to build virtual models to achieve dynamic simulation. - Artificial Intelligence and Algorithms A
Apply machine learning and algorithms to predictively analyze data, diagnose problems, and modernize operational processes.
The Rise of the Digital Twin
The core of smart manufacturing is to improve efficiency and quality and reduce costs while reducing reliance on human labor. CNC machine tools often constrain production optimization in traditional machining processes due to a lack of data collection capabilities and system compatibility issues. By introducing artificial intelligence and digital twin technology to CNC machine tools, the industry is beginning to move toward intelligence.
The application of digital twin technology covers real-time monitoring of machine tool status, digital collection and return of operational data, and intelligent optimization of manufacturing processes. For example, a CNC machine tool that runs intelligently using the synergy of an industrial manufacturing simulation engine, an edge LI system, and a cloud twin system can sense the machining process in real-time and generate detailed digital records. These records improve the process’s traceability and provide data support for large-scale promotion and replication.
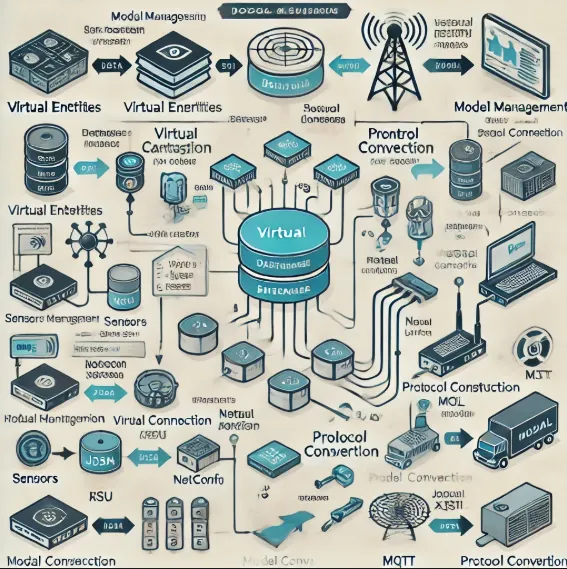
Pain Points and Solution Paths for Machining Intelligence
In the current machining industry, major challenges include a lack of simplicity, compatibility, and intelligence. Trivial process adjustment procedures and operational experience are difficult to migrate, making the industry limited. In addition, compatibility issues between different vendors and versions of CNC machine systems hinder flexibility and efficiency in the manufacturing chain.
The traditional automated manufacturing system has a high degree of dependence on the operator, and this status quo is particularly insufficient in the context of increasing demand for flexible and intelligent manufacturing. The intervention of artificial intelligence technology has changed this situation, intelligent CNC machine tool systems can learn the operation mode of workers, through real-time adjustment to adapt to different processing needs, thus realizing the decoupling of tasks and hardware.
Data-Driven Intelligent Manufacturing Systems
Data is the key to driving the development of smart manufacturing. In traditional CNC machine tools, the data acquisition capacity is limited, which not only restricts process optimization, but also leads to a high degree of dependence on experience in the production process. The intelligent CNC machine tool system can not only collect rich process data through digital contraction technology, but also use artificial intelligence algorithms for real-time optimization.
For example, in terms of tool management, the intelligent machine tool generates a digital LiSheng model for each tool, recording its full life cycle usage status. When a tool needs to be replaced, the system automatically adjusts the process parameters without the need to replace the entire set of tools, thus reducing waste and enhancing production flexibility.
Side Cloud Collaboration and Platformized Services
As smart manufacturing evolves, IT and OT (operating technology) are converging. Networked machine tools facilitate data sharing and large model training, and make it possible for edge LISON systems to operate in concert with cloud LISON systems. Through this collaborative mechanism, companies can build large-scale smart factories and realize the full intelligence of the production process.
For example, the cloud LISON system can be divided into a metafactory layer, an infrastructure layer, a LISON layer, and a business layer, which are responsible for programming, data management microservice generation, and business scenario adaptation, respectively. Through this multi-layer architecture, enterprises can efficiently realize the intelligent management of the whole chain from requirement definition to product delivery.
Transitioning from Process to Object-Oriented
Traditional CNC machine tool programming language G code, invented in the 1950s, is a process-oriented “way to describe the manufacturing process. While the digital Li Sheng technology uses an object-oriented approach, by generating a digital model of each entity (e.g., tools, fog parts, machine tools), it greatly improves programming efficiency and staff activity. This transformation not only solves the silo effect in traditional manufacturing but also lays the foundation for intelligent manufacturing mode.
In the future, the full landing of intelligent manufacturing will further promote the machining industry from traditional automation to a truly intelligent transformation through the deep integration of data-driven and artificial intelligence technology to achieve the industry’s cost reduction and efficiency and scale services.
